[OS]Concurrency(1): Introduction
by
“Operating Systems: Principle & Practice”와 “Operating System: Three Easy Pieces”를 보며 메모했습니다.
Concurrency?
주요 주제는 multi-threading입니다. 우선 thread란 어떤 running process에 대한 abstraction이라고 할 수 있는데, 기존 single thread 프로그램과 멀티스레드 프로그램의 차이점은 멀티스레드는 동시에 여러 개의 point of execution을 가질 수 있다는 점입니다.
thread와 process의 차이점
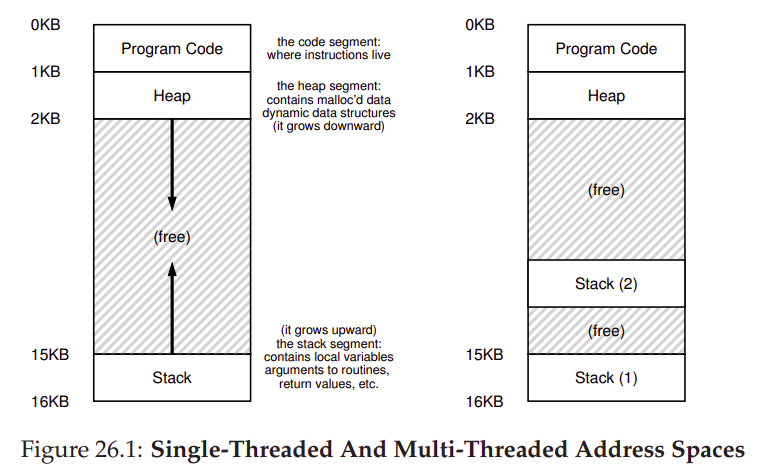
- address space가 같습니다. 즉, context switch에서 사용 중인 page table을 바꿀 필요가 없습니다.
- stack에 있어서 싱글스레드 프로그램에서는 address space에 스택이 하나만 있지만, 멀티스레드 프로그램에는 스레드마다 하나씩 해서 여러 개의 스택이 있습니다.
Thread Context Switch
한 스레드를 실행하다가 다른 스레드를 실행할 때 일어나는 일입니다. 현재 running thread의 실행을 멈추고 다른 스레드의 실행을 resume하는데, 현재 running thread의 registers를 TCB에 저장하고 stack도 저장합니다. 그 다음 다른 스레드의 register를 그 스레드의 TCB에서 불러오고 stack 도 불러옵니다. 이 과정에서 다음 질문들에 답을 할 수 있어야 합니다.
- What triggers a context switch?
- How does a voluntary context switch(e.g. a call to thread_yield) work?
- How does an involuntary context switch differ from a voluntary one?
- What thread should the scheduler choose to run next?
이들 중 1, 2, 3번은 mechanism에 대한 것이고 마지막은 policy에 대한 것입니다. 시스템마다 요구되는 policy가 다를 수 있는데, mechanism과 policy를 분리시켜서 구현해야, mechanism은 유지하면서 policy를 바꾸거나 발전시키는 작업이 쉽습니다. 실제 구현에서 중요합니다.
What triggers a context switch?
Voluntary, Involuntary가 있습니다.
- 전자는 스레드가 thread_yield 함수 등을 호출해서 스스로 resource를 포기하는 경우입니다. thread_join(main thread가 다른 스레드들을 기다리느라 yield함)이나 thread_exit등도 있습니다.
- 후자는 interrupt나 processor exception가 interrupt handler를 invoke하는 경우, 혹은 다른 thread가 더 높은 우선순위를 가지는 경우입니다. 가령 IO event등은 interrupt를 시킵니다. 또한 Hardware timer가 있어서 주기적으로 processor를 interrupt하는데, 한 스레드가 너무 processor를 오래 점유한다면 running thread를 바꾸게 됩니다.
How does a voluntary context switch(e.g. a call to thread_yield) work?
voluntary context switch에는 thread_yield, thread_join 등의 경우가 있습니다.
thread_yield시에는 우선 interrupt를 disable하고, 다음으로 실행할 스레드를 리스트에서 선택하고, running thread의 상태를 ready로 바꾸고, thread_switch를 합니다.- thread_switch: 레지스터 값들을 스택에 저장한 뒤 스택 포인터를 old thread의 TCB에 저장하고 새로운 스택으로 바꾼 뒤 새 스택의 레지스터 값들을 가져오기
- 그 뒤 finished list에 있는 스레드를 삭제합니다. 마지막으로 interrupt를 다시 enable합니다.
How does an involuntary context switch differ from a voluntary one?
방식은 interrupt나 trap이 thread switch를 user <-> kernel 사이에서 일으킬 때와 비슷합니다.
- Save the state
- Run the kernel’s handler: 이미 kernel mode에 있으므로, user mode->kernel mode의 전환은 필요없습니다. stack pointer를 kernel의 interrupt stack으로 이동할 필요는 없고, 대신 saved state나 handler variables?를 현재 스택에 push하고 현재 stack pointer부터 시작합니다.
-
Restore the state: 다음 ready thread의 register를 다시 복구합니다.
- Question. Kernel threads 간의 switch와 user-mode transfer의 차이점은?
- mode switching에서는 stack을 바꾸고, interrupt handling에 mode switching 필요합니다.
- 반면 kernel thread에서 kernel handler로 바꿀 때에는 stack을 바꿀 필요가 없습니다.
User-level Threads
- kernel support를 통해 user-level thread 구현
- Hybrid Thread Join
- Per-process Kernel Threads: 코어마다 kernel thread를 하나씩 생성하고 user thread는 이걸 공유해서 사용합니다.
- Scheduler Activations: 윈도우에서 도입했다고 합니다.
- kernel support 없이 user-level thread 구현할 경우 장단점은? (green thread 등이 있는데, 라이브러리가 context switch를 합니다)
- 장: ?
- 단: 너무 많습니다. 가령, 하나의 user thread가 blocking을 하면 나머지도 다 쉬어야 합니다.
Alternative Abstractions
Asynchronous I/O and Event-Driven Programming
Thread 대신 event를 이용합니다. single-threaded program이 latency가 긴 I/O 장치 요청이 오면 I/O를 다른 processing을 가지고 overlapping합니다.
- event-driven programming vs. threads
- 둘의 차이?
- state가 연속적인지 / TCB에 담기는지의 차이
- state save/store가 명시적으로 앱에 의해 처리되는지 / thread system에 의해 자동으로 처리되는지의 차이
- 장단점?
- performance: high-latency I/O devices 를 다루는 데에는 event-driven이 더 좋을 수 있습니다.
- performance: 멀티코어를 잘 쓰기 위해서는 스레드가 좋습니다.
- responsiveness: 스레드는 어떤 일을 background로 돌리기가 쉬워서 더 responsiveness가 좋습니다.
- program structure: thread를 사용하는 편이 각 task 처리를 독립적이고 병렬적으로 생각할 수 있어서 프로그래밍이 더 쉽다고 합니다.
Data parallel programming
data set의 서로 다른 부분에 접근하게 해서 병렬적으로 데이터에 대한 연산을 수행합니다.
Subscribe via RSS
